Periodontic Dentistry
Gum disease is a threat to your oral health. Our mouths are full of bacteria. These bacteria, along with mucus and other particles, constantly form a sticky, colorless "plaque" on teeth. Brushing and flossing help get rid of plaque. Plaque that is not removed can harden and form bacteria-harboring "tartar" that brushing doesn't clean. Only a professional cleaning by a dentist or dental hygienist can remove tartar.
The longer plaque and tartar are on teeth, the more harmful they become. The bacteria cause inflammation of the gums that is called "gingivitis." In gingivitis, the gums become red, swollen and can bleed easily. Gingivitis is a mild form of gum disease that can usually be reversed with daily brushing and flossing, and regular cleaning by a dentist or dental hygienist. This form of gum disease does not include any loss of bone and tissue that hold teeth in place.
When gingivitis is not treated, it can advance to "periodontitis" (which means "inflammation around the tooth.") In periodontitis, gums pull away from the teeth and form "pockets" that are infected. The body's immune system fights the bacteria as the plaque spreads and grows below the gum line. Bacterial toxins and the body's enzymes fighting the infection actually start to break down the bone and connective tissue that hold teeth in place. If not treated, the bones, gums, and connective tissue that support the teeth are destroyed. The teeth may eventually become loose and have to be removed.
Treatments in Periodontic Dentistry
At Phuket Smile Signature, gum treatments performed by our gum dentists or periodontists include:
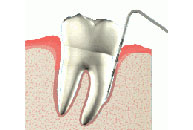 |
Deep Cleaning
The dentist removes the plaque through a cleaning method called scaling and root planing. Scaling means scraping off the tartar from above and below the gum line. Root planing and deep cleaning in quadrants gets rid of rough spots on the tooth root where the germs gather, and helps remove bacteria that contribute to the disease.
Deep Cleaning and Root Planning is used to treat and prevent gum inflammation, gum recession and gum diseases.
|
 |
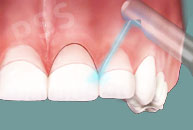
Periodontal Surgery
Periodontal surgery might be necessary if inflammation and deep pockets remain following treatment with deep cleaning and medications. A periodontist may perform flap surgery to remove tartar deposits in deep pockets or to reduce the periodontal pocket and make it easier for the patient, dentist, and hygienist to keep the area clean. This common surgery involves lifting back the gums and removing the tartar. The gums are then sutured back in place so that the tissue fits around the tooth again.
|
  |
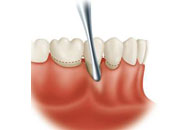
Crown Lenghtening & Gingivectomy
Some people have a lot of gum tissue around their upper teeth. Dentists call this "gummy smile." This also can be treated with crown lengthening or gingivectomy. It also can happen when a crown or filling falls out of a tooth and there is decay underneath. To place a filling or crown, dentist needs to expose more of the tooth. This is done by removing some gum tissue or bone with crown lenghtening or gingivectomy
Gingivectomy is the procedure whereby excess gums is removed. Crown lengthening is done when a tooth needs to be exposed more above the gum line.
Crown lengthening and gingivectomy is done using local anesthesia. How long it takes will depend on the number of teeth that need treatment. Even if only one tooth is involved, gum surgery typically includes neighboring teeth, too. That allows the tissues to be reshaped gradually. If both bone and soft tissue are removed, the procedure will take longer than if only soft tissue is removed.
The periodontist will make cuts that will pull the gums away from the teeth. This will expose the roots of the teeth and the surrounding bone. In some cases, simply removing a little gum tissue will expose enough tooth for your dentist to place a crown or filling. However, in most cases, the periodontist will need to remove some bone from around the roots of the teeth. Once the periodontist has exposed enough tooth, the surgical area will be washed with sterile salt water and the gums will be stitched together. |
 |
Gum Grafts
Gum recession is the process in which the tissue that surrounds the teeth pulls away from a tooth, exposing more of the tooth or the tooth's root. The most common method is cut and removed the gum from the selected area. Then, the gum will be stitched to the gum tissue surrounding the surgery site. |
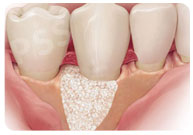 |
Bone Grafts
Bone Grafting is a way to replace or encourage new growth of bone or gum tissue that had been destroyed. A technique that can be used with bone grafting is called guided tissue regeneration, in which a small piece of mesh-like fabric is inserted between the bone and gum tissue. This keeps the gum tissue from growing into the area where the bone should be, allowing the bone and connective tissue to regrow. |
|





